Tissues & Organs
Tissues & Organs
Epithelial Tissue
Simple Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Found lining internal and external surfaces (i.e. blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lung alveoli, peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities
Kidney | loop of Henle, Bowman’s Capsule
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Found lining surface if ovary, lens, ducts of glands (i.e. sebaceous glands)
Kidney | collection tubules in kidney
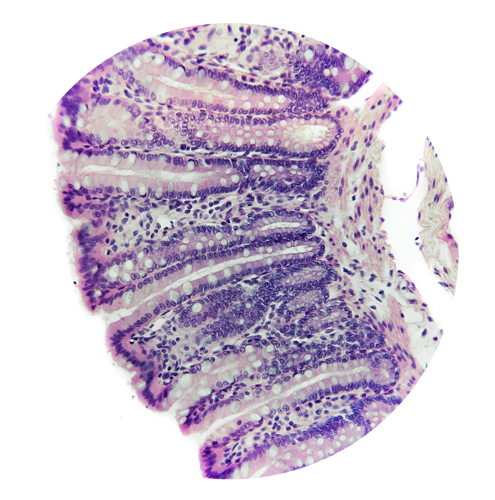
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Ciliated | found lining digestive system, small bronchi, uterus, oviducts, testis
Non-Ciliated | found lining gall bladder, ducts of large glands (i.e. salivary glands),
Kidney | papillary Ducts (Ducts of Bellini)
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Ciliated – found lining trachea, bronchi, auditory tube, tympanic cavity, nasal cavity
Non-Ciliated – found lining epididymis
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Keratinized | found lining skin
Layers of the Skin | stratum germinativum, stratum spinosum, granular stratum granulosum, hyaline stratum lucidum, cornified stratum granulosum
Non-keratinized | found lining mouth, oral pharynx, esophagus, vocal chords, vagina
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Found lining ducts of sweat glands, testis
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Uncommon, found lining conjunctiva of eye, large excretory ducts (i.e. bile ducts), male urethra
Transitional Epithelium
Found lining the urinary bladder, Key ID – dome shaped/binucleated cells
Glands
Exocrine Glands
Unicellular Glands
Goblet Cell | found lining digestive and respiratory track, secretes mucous
Multicellular Glands
Simple Tubular (Branched) Gland | gastric glands found in stomach containing three types of secretory cells – epithelial mucous cells, parietal cells (HCl), chief cells (pepsin)
Simple Tubular Gland | found in large intestine
Compound Acinar (Branched) Gland | exocrine pancreatic gland
Compound Tubuloacinar (Branched) Gland | salivary gland
Endocrine Glands
Ductless glands composed of clumps or chords of secretory cells secreting hormones into bloodstream
Islets of Langerhans | alpha (glucagon) and beta (insulin) cells